EU Commission Forecasts Assume 'No Deal' Outcome to Post-Brexit Trade Negotiations, see UK GDP Lagging that of Euro Area in 2021
- EU and UK to part on WTO terms says EU Commission
- EU GDP growth to outpace UK GDP growth
- UK debt to rise to 107% of GDP

Image: Photographer: Bryan R. Smith. © European Union, 2020. Source: EC - Audiovisual Service
The European Commission has released its latest economic forecasts for the EU, Euro Area and the UK, with projections built on an assumption the EU and UK will fail to strike a post-Brexit trade deal before year-end.
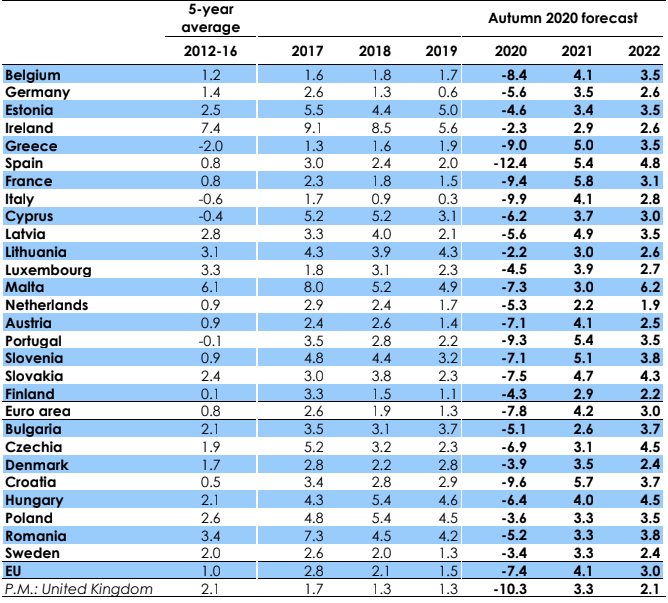
The EU has cut its 2021 Euro Area growth forecasts to 4.2% from 6.1% previously in their latest European Economic Forecast update, which also shows they expect debt to remain at 100% of GDP until 2022.
The Commission warned of rising economic uncertainty as a result of a resurgent covid-19 virus and called on EU member states to prioritise putting in motion the historic rescue fund agreed earlier this year.
Notably, the EU Commission says their forecasts make a technical assumption there will be no free trade deal struck with the UK and therefore the two sides will trade on WTO terms from January 01.
"Without prejudice to the ongoing negotiations, projections over the forecast period are based on the assumption that the EU and the UK will trade on WTO MFN rules (‘WTO assumption’) from 1 January 2021 onwards," says the report.
"The assumed move to this new trade relationship, which will be significantly less beneficial than the current situation, is expected to slow down the recovery considerably in 2021 and 2022," the report adds.
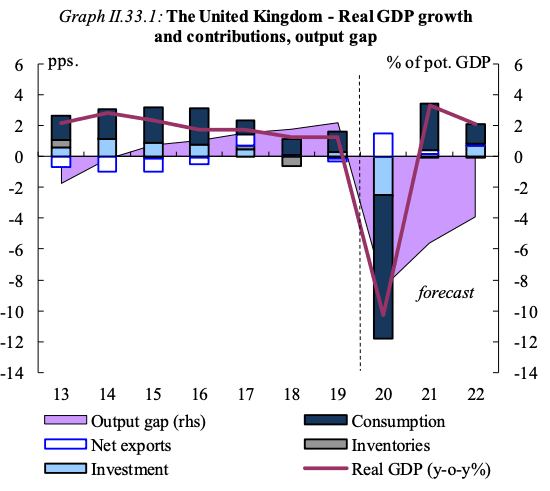
According to the EU Commission's economists, the UK's GDP growth is expected to slow down significantly in the last quarter of 2020.
The Commission expects business investment, which has already been weak in the past years, to rebound only slowly as businesses have to deal with the consequences of
the pandemic and the new trade relations with the EU.
Job losses and lower real wages are expected to negatively affect private consumption.
Government consumption is forecast to contribute positively to growth over the next two years. Their calculations show the government has provided support to the economy worth 10% of GDP via a fiscal package to counter the negative impacts of the pandemic, while liquidity measures amount to about 16% of GDP in the fiscal year 2020-21.
The Commission forecasts UK GDP growth to increase by 3.25% in 2021, and by 2% in 2022.
In the fourth quarter of 2022, UK GDP is projected by the Commission to still be 5% below the level of the fourth quarter of 2019. It is unclear however whether the second lockdown has been factored into the broader economic assumptions, suggesting a risk that these projections are too generous.
After growing 1.3% in 2019, GDP is forecast to contract by 10.25% in 2020, meaning the UK is expected to suffer the 2nd deepest recession in Europe this year, behind Spain. The Bank of England meanwhile today released data showing they forecast GDP growth in 2020 of -11% (a downgrade from the previous -9.5%).
"A potential trade agreement between the EU and the UK constitutes an upside risk for the forecast, whereas a less smooth transition to the new trade relationship would additionally weigh on growth," says the Commission.
Due to government policies supporting employees and the self-employed, unemployment is expected to increase only moderately in 2020, to 5.0% on average.
But, a slower-than-expecged recovery in 2021 and support terminating, unemployment is expected to increase sharply in 2021 to 7.3%. The forecasts were however made before the announcement of an extension to the furlough scheme for the month of November as the government seeks to minimise the impact of a second lockdown in England.
The Commission forecasts CPI inflation to ease to 0.9 % in 2020, mainly due to lower energy and service prices.
Inflation is projected to increase to 2.3% in 2021 and 2.9% in 2022, partly as a result of higher prices for imports resulting from the new trade barriers.
Looking at UK government debt dynamics, the general government deficit is forecast to increase from 2.8% in 2019-2020 to 14¾ % in 2020-2021, significantly higher than at the height of the financial crisis. The deficit is forecast to fall to 8¼ % in 2021-2022 and to 7¼ % in 2022-23.
The additional fiscal measures and the expected fall in GDP lead to an expected general government debt-to-GDP ratio of 107.5% in 2020-2021, up from 84.5% in 2019-2020.
Debt is projected to increase further over the forecast period to 113.5%.